Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint (aka gonarthrosis or abbreviated DOA)- degenerative-dystrophic disease of the knee joint, which is characterized by a chronic, persistently progressive course, damage to all anatomical elements (hyaline cartilage, periarticular bone structures, synovial membrane, capsule and joint ligaments) and articular deformity, to a lesser extentLeads to speed and often disability.
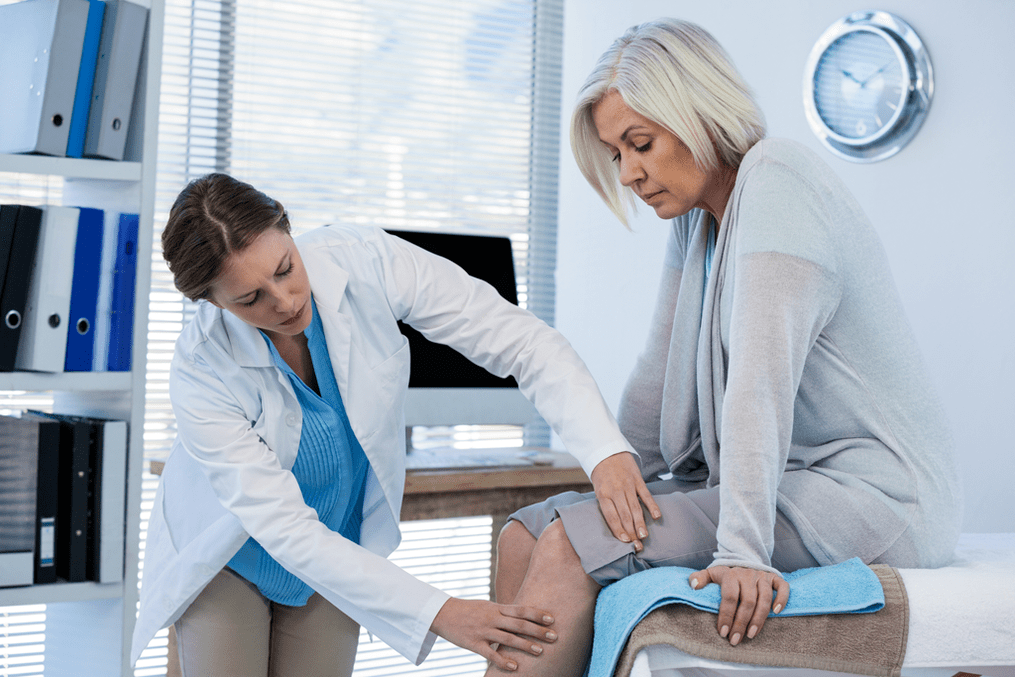

The disease begins with changes in the articular cartilage, causing the articular surface of the bones to dislodge. Malnutrition and loss of elasticity lead to its dystrophy (thinning) and resorption, while the bone tissue of the articular surfaces is exposed, The sliding is disturbed, the articular knee gap narrows, the biomechanics of the joint changes. The synovial membrane that lines the joint and produces synovial fluid (which nourishes the cartilage and acts as a physical lubricant) becomes irritated. There is an increase in its volume in the joint (synovitis). Against the background of narrowing of the joint space, the volume of the joint decreases, synovial fluid stretches the back wall of the joint capsule, and a Baker's cyst is formed. (which, reaching a large size, can cause pain in the popliteal fossa). The thin and delicate tissue of the joint capsule is replaced by thick connective tissue, the shape of the joint changes. Periarticular bone tissue increases, osteophytes (pathological bone growth) are formed. Blood circulation in the periarticular tissues is impaired, under-Oxidized metabolic products that irritate chemoreceptors accumulate in them, and a persistent pain syndrome develops. Against the background of changes in the anatomy of the joint, the surrounding muscles are violated, hypotrophy and cramps appear, And the gait is disturbed. There is a persistent limitation of the range of motion in the joint (narrowing), sometimes so pronounced that only rocking movements (stiffness) or a complete absence of movements (ankylosis) are possible.
Regarding arthrosis of the knee joint, we can say that this is a fairly common disease: it affects 10% of the entire population of the planet, and every third person over 60 years old affects it.
due to gonarthrosis
- Bone and joint injuries.
- Inflammatory diseases of the joints (rheumatoid arthritis, chlamydial arthritis, gout).
- Violation of mineral metabolism in various endocrinopathies (diabetes mellitus, diseases of the parathyroid glands, hemochromatosis).
- Diseases of the muscular system and neuropathy (Charcot's disease).
In addition to the main reasons, there are also adverse background factors for the development of gonarthrosis, which include:
- overweight (literally puts pressure on the lower limbs);
- age (mainly elderly people are more susceptible to this disease);
- female sex (according to statistics, women are sick more often);
- Increase in sports and professional physical activity.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
- Pain that increases with walking and subsides with rest.
- Difficulty in habitual, physical activity in the joints.
- Characteristic "crunch" in the joints.
- Joint enlargement and visual distortion.
stages of gonarthrosis
.png)
There are several stages of arthrosis:
- In the first stage, the person experiences only symptoms such asa little restlessnessor "heaviness" in the knee, trouble walking long distances or increased physical exertion. X-ray examination will reveal less: only a slight narrowing of the joint space can be detected, no other changes will occur. At the very beginning of the defeat of arthrosis of the joint, a person does not turn to specialists, without attaching special importance to the symptoms that appear.
- For the second stage of arthrosis of the knee joint,direct pain, the severity of which subsides at rest. The difficulty of movements in the joints is manifested, when walking, a characteristic "creak" is heard (from the patient you can hear a common phrase in everyday life - "creak of the knees"). When performing radiography, clearly distinct narrowing of the joint space and single osteophytes are found.
- with the transition to the next, third stage of gonarthrosis,Symptoms of pain will constantly bother the patient, including at rest, is a violation of the configuration of the joints, i. e. deformity, aggravated by edema at the time of joining the inflammation. On the radiograph, a moderate narrowing of the joint space and numerous osteophytes are determined. In the third stage, several firstSeek medical help from time to time, because quality of life is significantly affected by pain and difficulty walking normally.
- The fourth stage of arthrosis of the knee joint is accompanied byunquenchable pain. . . Minimal attempts to move become a difficult test for a person, joint deformities are visually noticeable, walking is extremely difficult. Radiography reveals significant changes: joint space in the imagesPractically undetectable, numerous gross osteophytes, "articular mice" (fragments of bone falling into the joint cavity) are detected. This stage of gonarthrosis almost always leads to disability: often the result of the disease is complete fusion of the joint, This leads to instability and the formation of "false joints".
Who treats arthrosis of the knee joint?
Qualified medical care for gonarthrosis may be provided to the patient by a physician, rheumatologist and general practitioner (family doctor), but these specialists deal with the treatment of the knee joint for uncomplicated arthrosis.
When synovitis occurs or the treatment prescribed by the doctor does not give the desired effect, one cannot do without the help of an orthopedist. In situations where surgical care is required, a patient with arthrosis of the knee joint is given a special orthopedic and traumasent to the department.
How and how to treat arthrosis of the knee joint?
Currently known methods of treatment of patients with arthrosis of the knee joint are divided into non-drug conservative, medical and surgical.
non-drug methods
Many patients ask themselves the question: "How to deal with arthrosis of the knee joint without pills? " Answering this, we must regretfully state that gonarthrosis is a chronic disease, it is impossible to eliminate it forever. However, Several currently existing non-pharmacological (ie, without the use of drugs) methods of dealing with the disease can slow its progression and improve the patient's quality of life, especially when used in the early stages of the disease. goes.
With sufficient motivation to visit the doctor in a timely manner and to cure the patient, sometimes it is enough to eliminate the negative factors. The manifestation of the main symptoms is reduced.
elimination of pathological physical activity and, conversely,medical gymnasticsUsing rational physical programs they reduce the intensity of pain. Exercises to strengthen the quadriceps femoris have been shown to be comparable in effect to anti-inflammatory drugs.
If we treat arthrosis of the knee joint, it is necessary to strive forproper nutrition: Products containing large amounts of animal collagen (dietary types of meat and fish) and cartilage components (shrimp, crab, krill), fresh vegetables and fruits saturated with vegetable collagen and antioxidants help to improve the elastic properties of articular cartilageMillie, and a passion for smoked meats, marinades, preservatives, sweet and salty dishes, on the contrary, leads to disturbances of metabolic processes in the body and the accumulation of excess weight up to obesity.
Considering the most effective treatment for knee arthrosis, it is worth remembering such an effective treatment and prophylactic method.orthotics: Fixing knee pads, orthoses, elastic bandages and orthopedic insoles reduce and correctly distribute the load on the joint, reducing the intensity of pain. Walking stick as an effective relief of knee jointsIt is also recommended to use it. It should be in the hand opposite to the affected limb.
Comprehensive treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint also implies the appointment of very effective even with advanced forms of the disease.physical treatment. . . with wide use in various categories of patients suffering from arthrosis of any degree, it has proven its effectivenessmagnetotherapy: after several procedures, the intensity of pain decreases, as a result of improving blood circulation, reduction of edema and elimination of muscle spasms, the mobility of the joint increases. The effect of magnetotherapy is especially due to active inflammation in the joint. With the development is evident: the severity of edema is significantly reduced, the symptoms of synovitis return. Not so popular, but no less effective in treating the knee joint for arthrosis, as are physiotherapy methodslaser therapyAndcryotherapy(exposure to cold), which has a pronounced analgesic effect.
drug treatment
In the schemes of effective treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint, the following drugs are used.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), produced in the forms of external (various gels, ointments) and systemic use (tablets, suppositories, solutions), have long been proven their effectiveness in the treatment of osteoarthritis and are widely prescribed by doctors. Enzymatic levelsBut by inhibiting inflammation, they eliminate pain and swelling of the joints, and slow down the progression of the disease. With the initial manifestations of the disease, the local application of these drugs in combination with non-drug methods (therapeutic exercises, magnetotherapy)The use is effective. But with osteoarthritis of the knee joint, tablets, and sometimes injections of NSAIDs are indispensable. It should be remembered that prolonged systemic intake of NSAIDs leads to further exacerbation of ulcerative processes in the gastrointestinal tractcan, and in addition, negatively affects kidney and liver function. Therefore, patients taking NSAIDs for a long time should also be prescribed drugs that protect the gastric mucosa, and internal organs regularlythe laboratory performance ofShe does.
Glucocorticosteroids (GCS)- Hormonal drugs with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. They are recommended when previously prescribed NSAIDs to the patient do not cope with the elimination of the manifestations of inflammation. Being a potent anti-inflammatory agent, some of the GCS in the treatment of arthrosisThere are contraindications, as they can cause a number of significant side effects. In systemic forms with gonarthrosis, they are practically not prescribed. As a rule, for the effective treatment of arthrosis, GCS injections into periarticular pain points are meant, which increases the intensity of the fight against inflammation and reduces the risk of unwanted side effects of the drug. This manipulation can be performed by a rheumatologist or trauma specialist. With concomitant synovitis or rheumatoid arthritis, these drugs are injected directly into the joint. is injected. With a single administration of GCS, the effect of such treatment lasts for 1 month. According to the National Guidelines for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis, do not make more than three injections of the drug per year into the same joint.
with advanced, "neglected" osteoarthritis, when a person experiences unbearable pain that does not subside even at rest, disrupts normal sleep, and is not removed by NSAIDs, GCS and non-drug methods, so it is possible to determineopioid pain relievers. . . These drugs are to be used only with the prescription of a doctor, taking into account the appropriateness of their appointment in each case.
chondroprotectors(literally translated as "protecting cartilage"). This name is understood as various drugs, which are united by one property - a structural-modifying action, i. e. slowing down degenerative changes in cartilageand the ability to contract the joint space. They are produced in both forms for oral administration and for introduction into the joint cavity. Of course, these drugs do not work miracles and do not "grow" new cartilage, but they prevent its destructionTo obtain a lasting effect, they must be applied over a long period of time with regular courses several times a year.
Surgical treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
Often there are cases when, despite sufficiently complex treatment, the disease progresses, there is a persistent decrease in the quality of human life. In such situations, the patient begins to ask the question: "If the prescribed drugs help with arthrosis of the knee joint. "What to do if not? There is a syndrome and significant dysfunction of the joint, which cannot be eliminated with the use of complex conservative therapy, which is possible with the last, fourth degree of the disease.
The most popular type of surgical care for third and fourth degree arthrosis isEndoprosthetics, ie. removal of one's own joint with the simultaneous installation of a replacement metal prosthesis, the design of which is similar to the anatomy of the human knee joint. In this case, this type of surgicalA prerequisite for treatment is: the absence of gross deformities of the joint, the formation of "false joints", muscle contractions and severe muscle atrophy. In case of severe osteoporosis (significant decrease in bone mineral density), endoprosthetics are also not indicatedIs: "Chinese" bone will not withstand the introduction of metal pins, and rapid resorption (resorption) of bone tissue will begin at the site of their installation, pathological fractures may occur. Therefore, at a time the need to install an endoprosthesisBut the decision appears to be so important - it should be taken when the age and general condition of the human body still allows to perform the operation. According to the results of long-term studies, the duration of the effect of endoprosthetics in patients with advanced arthrosis, i. e. The absence of significant motor limitations and the temporary duration of maintaining a good quality of life is approximately ten years. The best results of surgical treatment are in people 45–75 years old with low body weight (less than 70 kg) and relatively high living standards. seen inHuh.
Despite the widespread use of knee arthroplasty, the results of such operations are often unsatisfactory, and the percentage of complications is high. This is due to the design features of the endoprosthesis and the complexity of surgical intervention (replacing the hip joint in technical termsVery easy.
Arthromedullary bypass- a hollow metal tube - the connection of the medullary canal of the femur with the cavity of the knee joint using a shunt. This allows fatty bone marrow from the lower third of the femur to enter the knee joint, nourishing and lubricating the cartilageAllows, thereby significantly reducing pain.
When changing the axis of the lower limb (but with a slight restriction of the range of motion), it is effectivecorrective osteotomy- Transition of the tibia with correction of its axis, followed by fixation with plates and screws in the desired position. At the same time, two goals are achieved - the normalization of biomechanics due to the restoration of the limb axis, as well as of bone fusionDuring activation of blood circulation and metabolism.
Summing up the above, I would like to note that the treatment of gonarthrosis is a complex social task. And although today medicine is not able to offer a drug that can get rid of it forever, or completely cure this disease. Other ways to recover from this condition, a healthy lifestyle, getting medical help on time and following the doctor's recommendations can stop its progression.



















































